Typhoid fever
TYPHOID FEVER (ENTERIC FEVER)
Definition: -
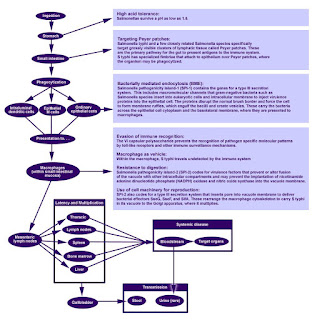
Typhoid fever is an infectious disease by salmonela typhi & salmonela paratyphi A,B
ü Which
is gram negative, non-spore forming bacilli .The bacilli may live
in gallbladder of carriers for month of year after clinical recovery
& pass intermittently in the stool.
ü Major
cause morbidity and mortality.
ü Food
water borne disease.
ü The
bacteria are deposited in water or food by a human carrier and then
spread to other people.
CAUSE OF TYPHOID FEVER
BACTERIA - Salmonella Typhi.
• Family-Enterobacteriacea.
•
Gram negative bacilii.
•
Best grows at 37 C
TRANSMISSION OF TYPHOID
Fecal-oral route:-
•
Close contact with patients or carriers.
• Contaminated
water and food.
• Flies
and cockroaches.
Does typhoid spread by kissing?
ü The
organisms can be transferred from person to person by both
direct (via saliva, fecal/oral spread, kissing)
and indirect contact (for example, using contaminated eating utensils)
ü It
occurs predominantly in association with poor sanitation and lack of clean
drinking water
How to diagnosis of typhoid by clinical features & laboratory
Clinical features:-
• Onset
may be insidious
• Incubation
period :- 10-14 day
1. First weeks
• High
fever 103–104° F :- continuous , stepladder fashion
• Headache
• Myalgia
• Relative
bradycardiya
• Constipation
• Diarrhoea
• Vomiting
2.
End of first week:-
• Ross
spots on the trunk
•
Enlarge spleen
•
Cough
• Stomach
pain
• Abdominal
distended
3.
End of second week :-
• Complication , Delirium
, coma & death
Complications of typhoid
• Perforation,
haemorrage
• Septicemia
• Bone
& joint infection
• Meningitis
• Cholicystitis
• Toxic
phenomena-nephritis
• Myocardidits
Investigation of typhoid fever
• Blood
count – Leucopenia with relative pymphocytosis.
• 1st
week – Blood culture positive
• 2nd
week – Widal test positive
• 3rd
week – Stool & urine culture positive
• Blood
count – Leucopenia with relative pymphocytosis.
• 1st
week – Blood culture positive
• 2nd
week – Widal test positive
• 3rd
week – Stool & urine culture positive
• NEW
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS:-
•
IDL Tubex detects IgM09
antibodies within few minutes
• Typhidot test that detects presence of
IgM and IgG in one hour (sensitivity>95%, Specificity 75%)
• Typhidot-M
that detects IgM only (sensitivity 90% and specificity 93%)
• Typhidot
rapid (sensitivity 85% and Specificity 99%) is a rapid 15 minute
immunochromatographic test to detect IgM.
•
IgM dipstick test
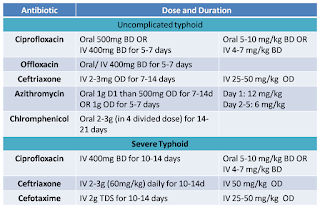
Management of typhoid fever
General: - Supportive care includes
• Maintenance
of adequate hydration. Antipyretics. Appropriate nutrition.
• Specific:
Antimicrobial therapy is the mainstay treatment.
Prevention of typhoid fever
CONTROL OF SANITATION
Protection & purification of drinking water supplies •
Improvement of basic sanitation • Promotion of food hygiene
• Best
prevention Scrub of them off your hands Best prevention Scrub them off your hands
• Simple
hand hygiene and washing can reduce several cases of Typhoid
• IMMUNIZATION
:-Vaccination recommended
Please do not forget to like , share & comments
We will be continue . visit:- https://drkaushar2.blogspot.com/










No comments:
For more information you like & comment